用户:Grotton JXz Donbrako/Psychology/Chapter 3
目录
页面介绍
本页面所转载文章出自APPsychPrep网站所分享幻灯片[1],由GJD转载。
转载时有改动,无任何原内容省略。
正文
Neuroanatomy
- Neuroanatomy refers to the study of the parts and function of neurons.
- Neurons are individual nerve cells that make up your central nervous system.
- Every neuron is made up of discrete parts.
- 神 经 元 玉 照.jpg
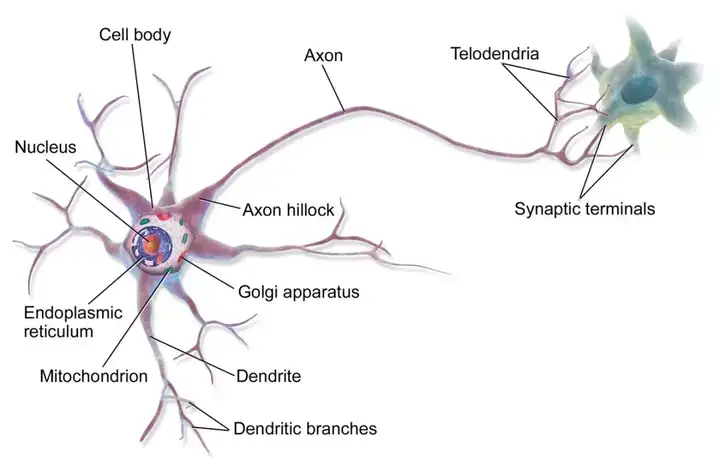
- Dendrites: Rootlike parts of the cell that stretch out from the cell body.
- Dendrites grow to make synaptic connections with other neurons.
- Cell Body: Contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to keep it living (mitochondria, nucleus, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, etc.).
- Axon': Wire-like structure ending in the terminal buttons that extends from the cell body.
- Myelin Sheath: A fatty covering around the axon of some neuron.
- Terminal Buttons: The branched end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters.
- Neurotransmitters: Chemicals contained in terminal buttons that enable neurons to communicate. Neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites on the dendrites of neurons like a key fits into a lock.
- Nodes of Ranvier: The small gaps between the myelin sheath are the Nodes of Ranvier. These gaps are where neural transmission takes place on myelinated neurons.
- Synapse: This is the gap between the terminal button and the dendrite.
- Synapse.jpg
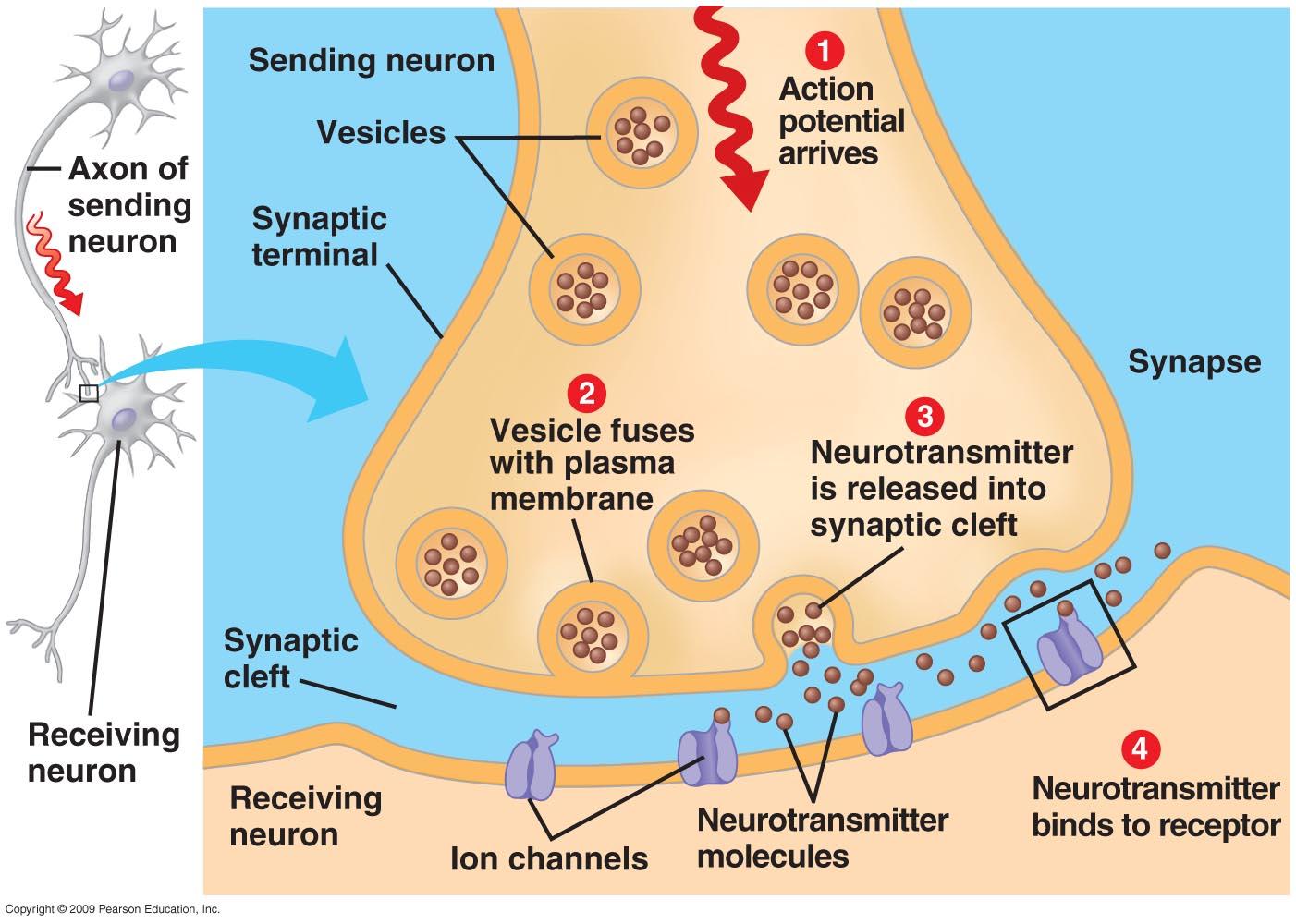
How a Neuron Fires
- Neural firing is an electrochemical process. Electricity travels within the cell from the dendrites to the terminal buttons.
- Neurotransmitters travel between cells in the synapses of neurons.
- Electricity does not jump across the synapse; neurotransmitters travel across.
- Neuron has a slightly negative charge (-70mV).
- Neurotransmitters from one neuron land on the dendrites of another neuron.
- The neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites.
- If the threshold is reached, the neuron becomes permeable to positive ions and they rush down the neuron causing it to fire.
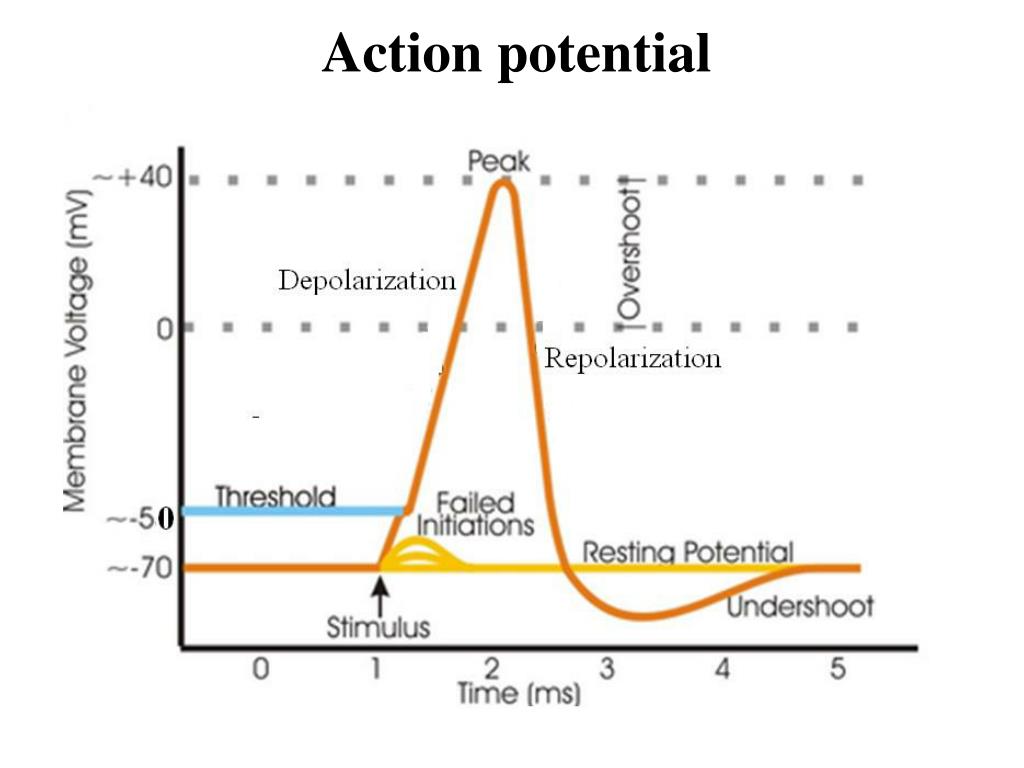
- All-or-nothing Principle: Neurons either fire or don't; this principle is called the all-or-nothing principle.
- A neuron is similar to a gun in that, you cannot shoot the gun just a little.
(Boolean型变量啊嗯)
- Neurotransmitters are chemicals held in the terminal buttons that travel across the synapse to the dendrite of another neuron.
- Some neurons are excitatory, some are inhibitory.
- Excitatory neurotransmitters make the next neuron fire.
- Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter.
- Inhibitory neurotransmitters prevent the next neuron firing.
- GABA(gamma-Aminobutyric acid) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter.
- Acetylcholine is involved in movement, memory function, and muscle contraction (particularly in the heart).
- Dopamine is involved in movement, alertness, attention, reward, and imbalances are associated with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer's disease.
- Endorphins are involved in pain control. They are the body's natural painkillers.
- Serotonin is involved in mood, sleep, pain, sensitivity, and arousal.
- Norepinephrine/Noradrenaline is involved in alertness/arousal.
Neurons (afferent, inter, efferent)
- Afferent/Sensory Neurons take information from our senses to the spinal cord.
- Interneuron, found in the spinal cord, relays signals between (afferent) sensory neurons, and (efferent) motor neurons; involved in the process of sensory-motor integration.
- Efferent Neurons are conducting cells that carry information from the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) to muscles and organs throughout the body.

- A subset of movements are controlled by direct transmission from afferent to efferent cells at the level of the spinal cord.
- Reflexes: Quick and involuntary responses to environmental stimuli.
Nervous System
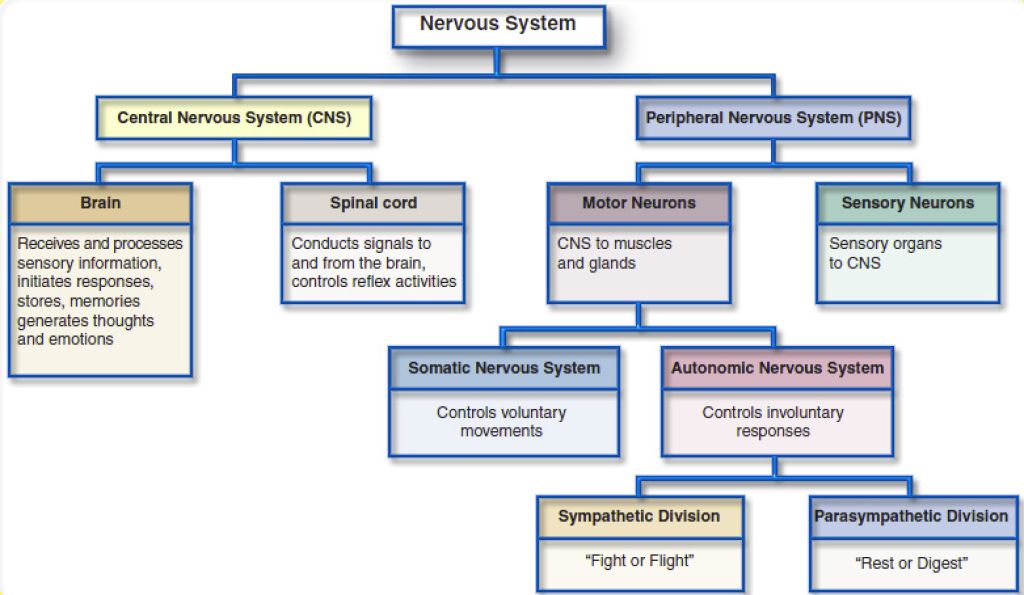
- The CNS (Central Nervous System) is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
- The PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) consists of all the other nerves in your body other than those in the brain and spinal cord.
- ↓The PNS的Motor Neurons is divided into two categories: the somatic and the autonomic. PNS还有Sensory Neurons,效果如其名。
- The somatic nervous system controls our voluntary muscle movements. The motor cortex of the brain sends impulses to the somatic nervous system, which controls the muscles that allow us to move.
- The autonomic nervous system is responsible for control of the bodily functions not consciously directed, such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes.
- (automatic)The sympathetic nervous system mobilizes our body to respond the stress. It is involuntary.
- This part of our nervous system carries messages to organs, glands, and muscles. The sympathetic nervous system controls heart rate, blood pressures, respiration, and slows non-vital functions such as digestion and reproductive organs.
- Also called the Fight or Flight System.
- The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for slowing down our body after a stress response.
- The parasympathetic nervous system puts on the brakes to slow down the body’s autonomic nervous system.
- Often referred to as the Rest and Digest System.
Brain
- Ways we can study the brain: Accidents, Lesions, Electroencephalogram, Computerized Axial Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Positron Emissions Tomography, Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Accident
- Accidents give clues about brain function.
理论上人为研究也有效果,但是咱不当做这事的是人。 Famous case (1848) of a railroad worker, Phineas Gage who was hit by a piece of rebar in the front of his head. Having sustained damaged to his frontal lobe, and having become highly emotional and impulsive after.- Doctors concluded that the frontal lobe was somehow regulating emotion.
- 扩展文章:真实的不死男:铁棍刺穿头颅却谈笑风生,死后被掘尸研究(文/快哉风)
Endocrine System
Genetics/Genetic Disorders=
(待补充)