用户:Grotton JXz Donbrako/Psychology/Chapter 4
页面介绍
本页面所转载文章出自APPsychPrep网站所分享幻灯片[1],由GJD转载。
转载时有改动,无任何原内容省略。
正文
- Sensation refers to the process of sensing our environment through touch, taste, sight, sound, and smell.
- Perception is the way we interpret these signals or sensations and make sense of everything around us.
Sensation
- Our senses: receptors in our eyes, skin, tongue, nose, receive stimuli from our environment.
- What is a stimulus?
- Energy transmitted from the environment (e.g., light, chemicals, pressure, heat).
- Transduction: Stimuli from the environment are transformed into neural impulses.
- Sensory adaptation is a decreasing responsiveness to stimuli due to constant stimulation (e.g., when standing in a noisy environment).
- Sensory habituation: Our perception of sensations is partially due to how focused we are on them.
- Cocktail Party Effect: Your ability to block out a lot of irrelevant stimuli in your environment.
Sensation: VISION
- Visible light is a small section of the electromagnetic spectrum
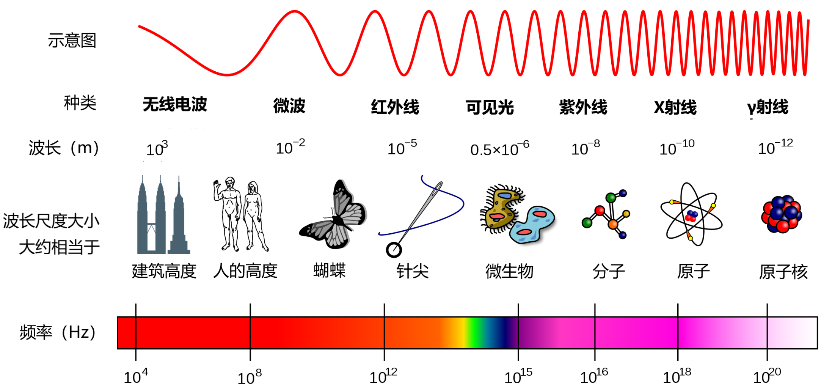
- Objects appear the color they do as a result of the wavelengths of light they reflect.
- A red shirt reflects red light and absorbs all other wavelengths.
- An object appears black because it absorbs all wavelengths.
- A object appears white because it reflects all wavelengths.
- The Cornea: Controls the light coming from the outside and focuses it onto the pupil.
- The Pupil: Is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.
- The Retina Is where the actual processing of the light occurs and is translated by rods and cones.
- The Fovea: A small depression in the retina where visual acuity is highest.
- The center of the field of vision is focused in this region, where retinal cones are particularly concentrated.
- Light enters the eye through the cornea.
- Light passes through the pupil.
- The lens focuses the light onto the retina.
- Light energy is converted into neural energy.
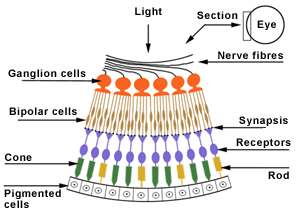
- Rods and Cones are photoreceptors in the human retina.
- Cones are activated by color.
- Rods are activated by white light and the absence of light.
- If rods and/or cones are stimulated by light, then they transmit this information to a second layer of cells called bipolar cells.
- Bipolar cells send this information to a layer of cells called ganglion cells.
- Ganglion cells make up our optic nerve which sends the information to the thalamus in our brain.

(待补充)